Gynecomastia comes from the Greek words gyne (woman) and mastos (breasts). The problem with gynecomastia is that is found only on the male chest. Every week, in our San Francisco Bay Area, Walnut Creek, California office, we see men wanting their gynecomastia removed. They are self conscious about going shirtless. Advanced gynecomastia is large enough to be a problem, even in clothing. Patients who lose significant amounts of weight will lose fat, but may not lose their gynecomastia. And when excess skin persists, so does the embarrassment. If you are concerned by extra fullness in your chest, Dr. Joseph Mele, in the San Francisco East Bay Area city of Walnut Creek, may be able to help.
Below is Colby’s Story. The video features my patient Colby. In it, he describes his motivation and personal experience with Gynecomastia Reduction Surgery. Beyond the Before & After is a series of short videos produced by the Aesthetic Society focused on the patient’s experience with cosmetic plastic surgery.
Male Breast Reduction Video Presentation
Every male is born with Gynecomastia. At birth, the condition is due to the mother’s hormones passing through the placenta. The female hormones designed to increase the size of the mother’s breasts also increase the amount a glandular tissue in the infant’s breast, resulting in a firm rubbery lump beneath the areola. Since babies do not normally make high levels of female hormones themselves, the hormone levels drop quickly after birth, and the gynecomastia resolves spontaneously.
Gynecomastia can return at puberty. The exact mechanism is unknown, but most likely it is in response to the breast tissue’s sensitivity to sex hormones. Moderate male adolescent breast development usually subsides in a few years, unless obesity is also present. Persistence of Adolescent Gynecomastia accounts for 25% of all gynecomastia cases. In rare cases, gynecomastia can also be the result of hormone producing tumors (often testicular).
Adult Gynecomastia can be the result of medications too. Many common drugs have been indicated including: steroids, some antidepressants, digitalis (Digoxin), furosemide (Lasix), estrogen, exogenous testosterone, alcohol, marijuana and heroin to name a few. Chemotherapy for prostate cancer can cause significant gynecomastia, and at times, frank breast development.
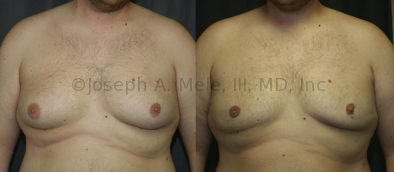
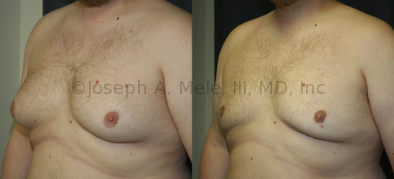
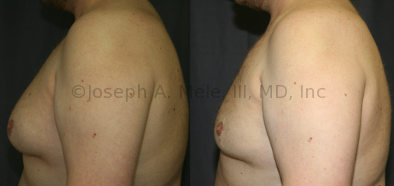
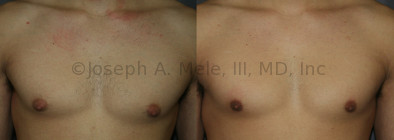
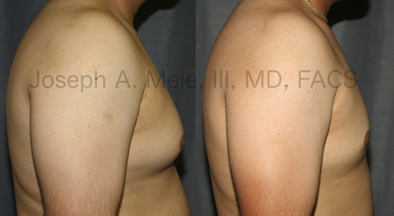
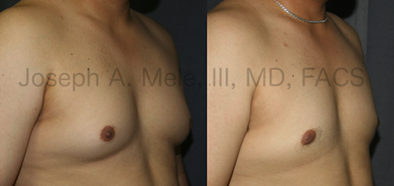
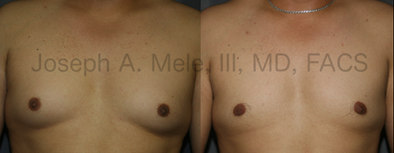
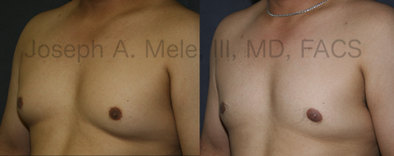
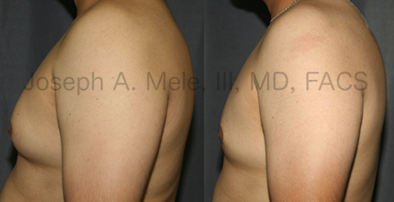
Gynecomastia Reduction Before and After Photos (Male Breast Reduction)
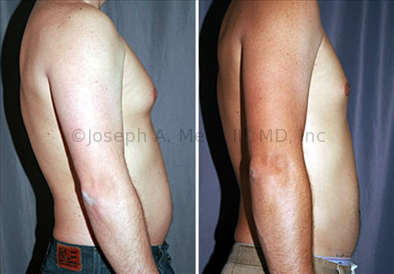
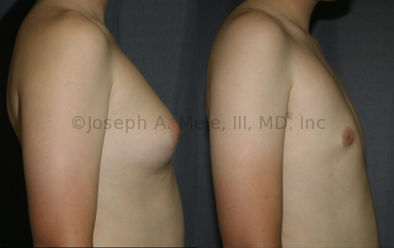
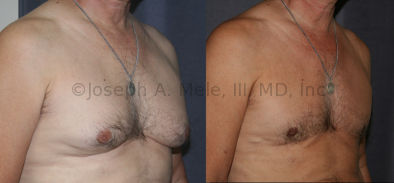
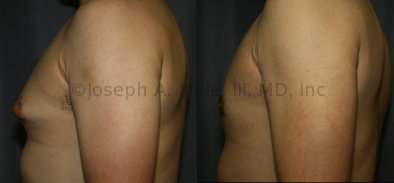
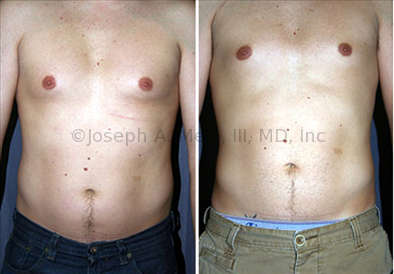
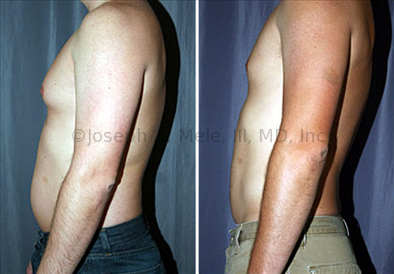
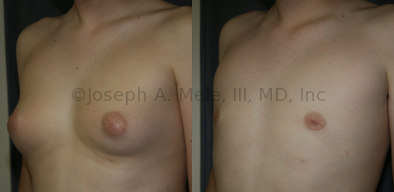
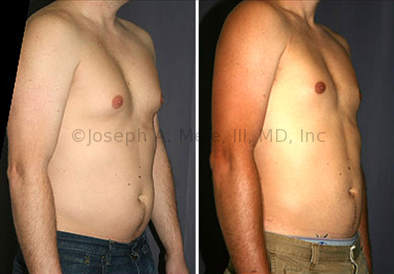
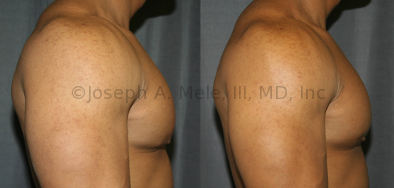
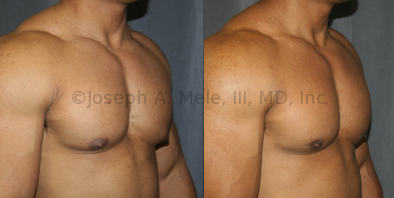
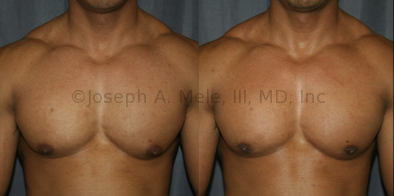
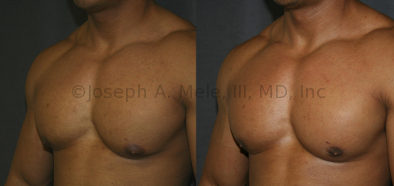
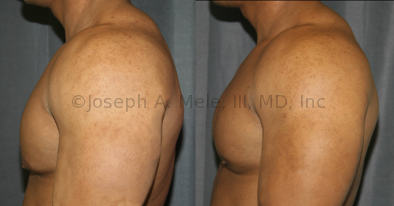
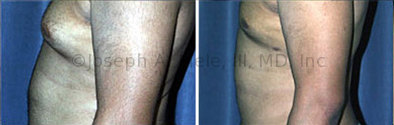
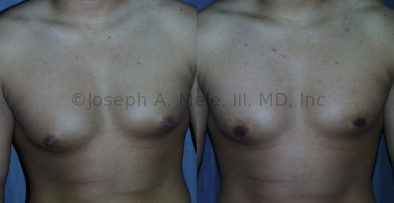
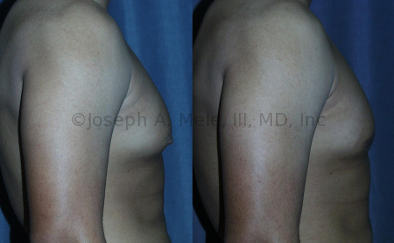
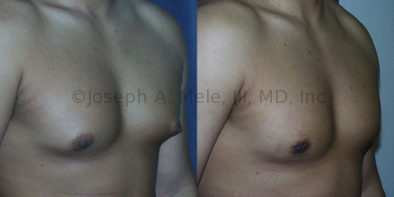
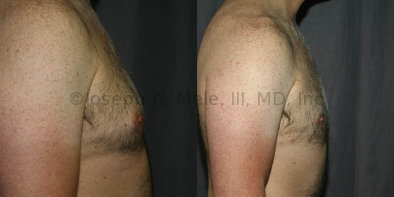
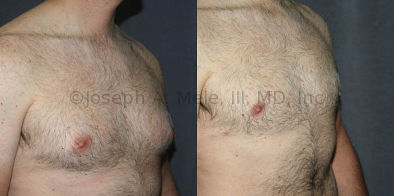
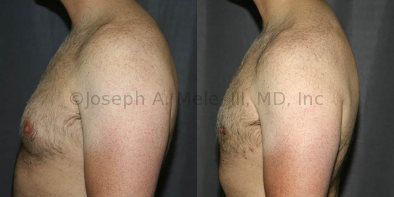
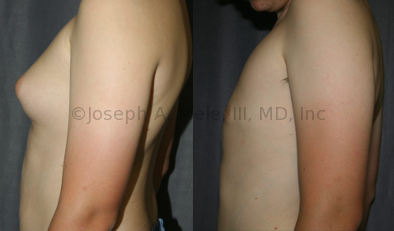
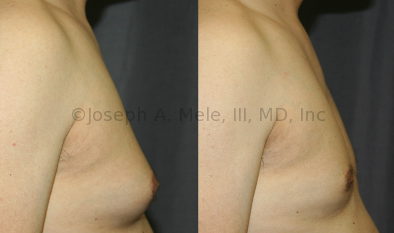
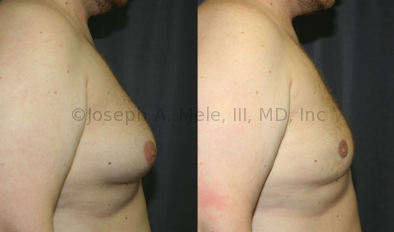
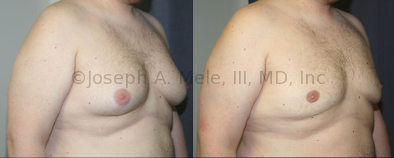
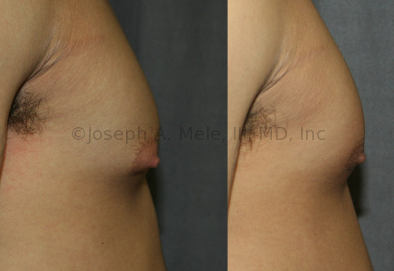
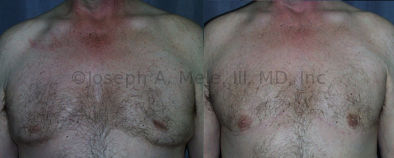
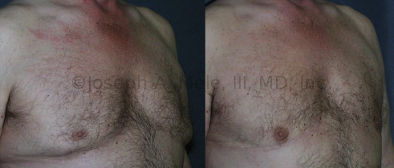
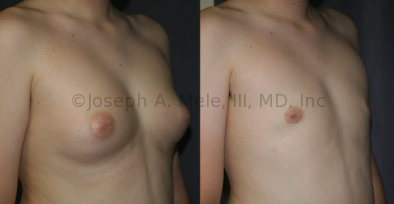
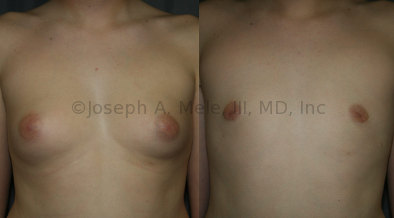
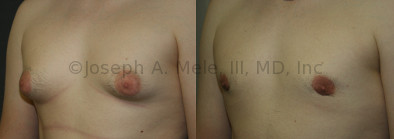
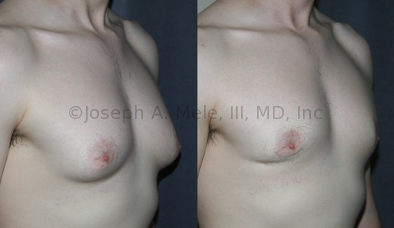
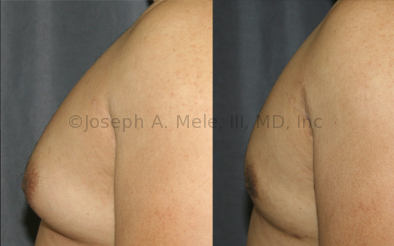
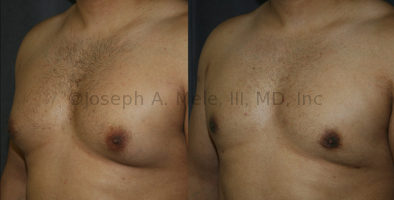
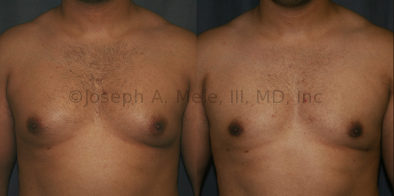
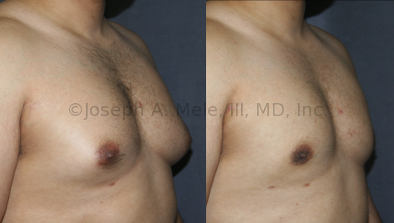
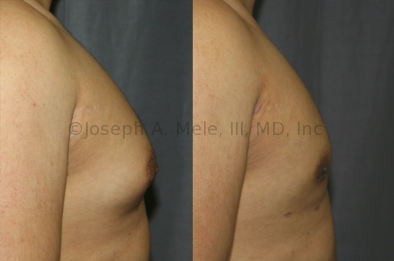
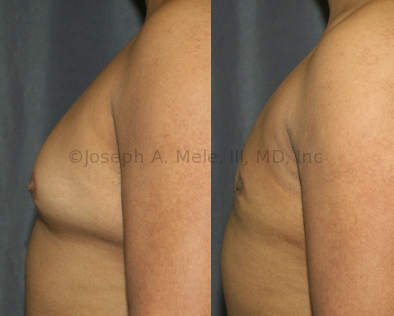
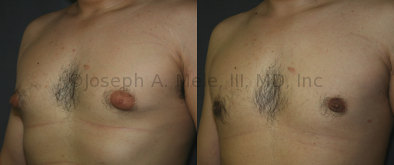
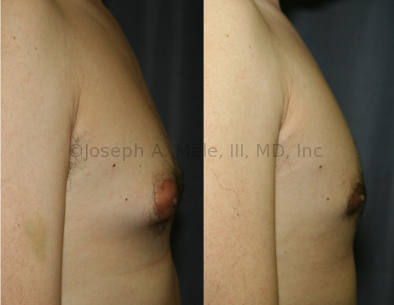
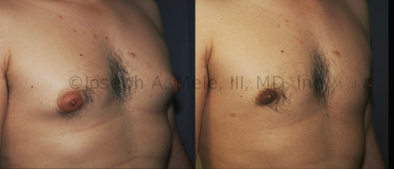
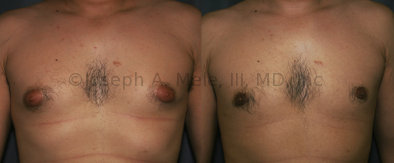
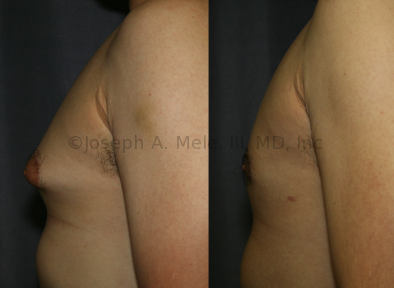
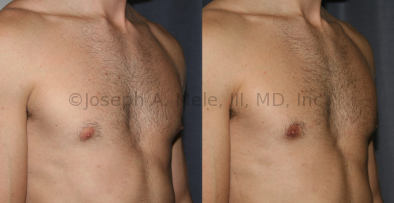
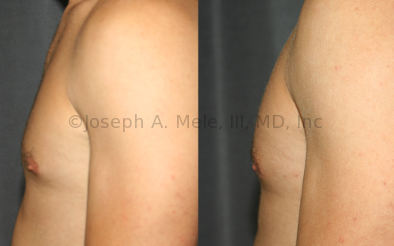
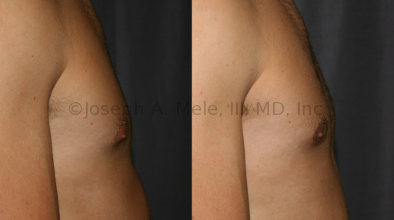
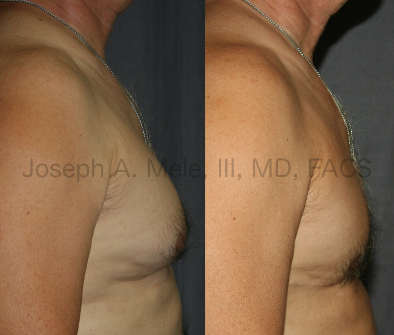
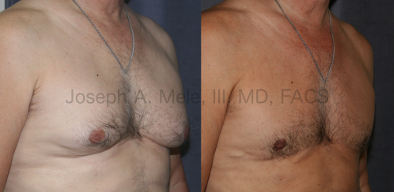
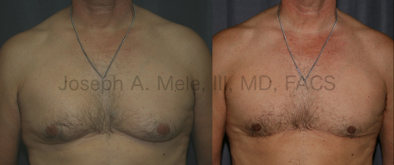
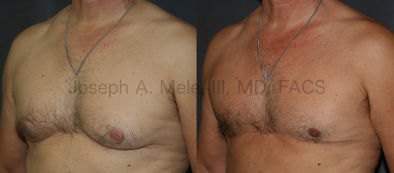
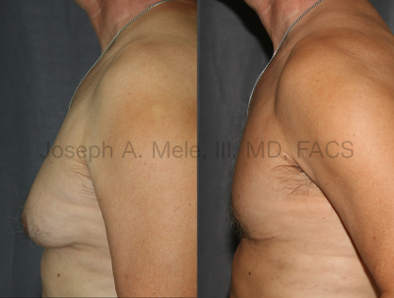
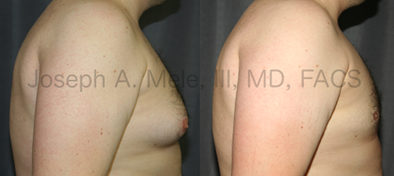
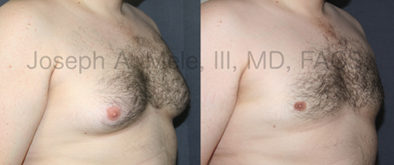
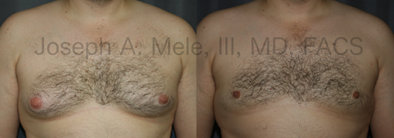
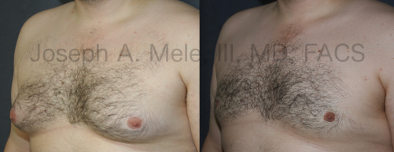
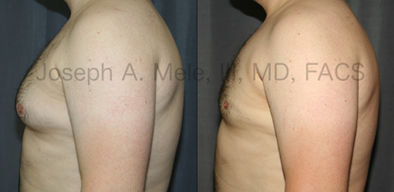
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
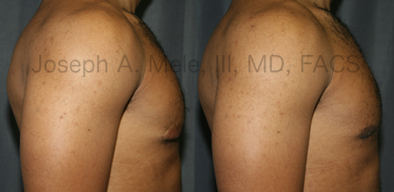
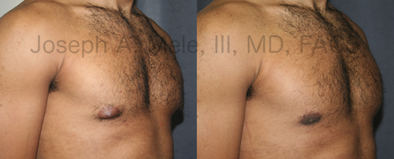
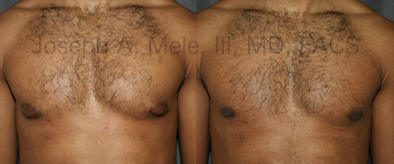
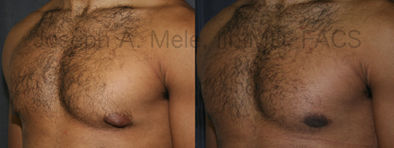
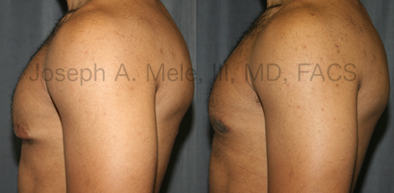
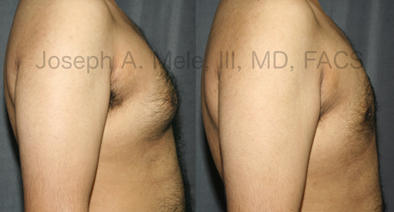
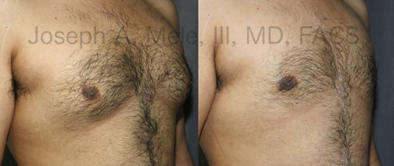
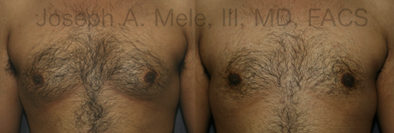
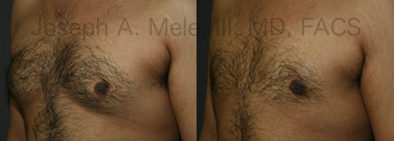
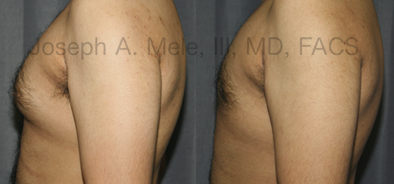
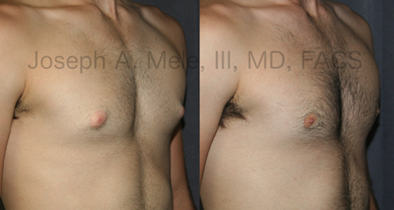
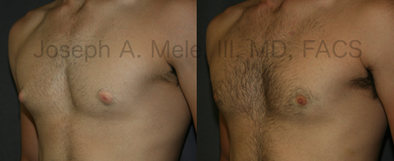
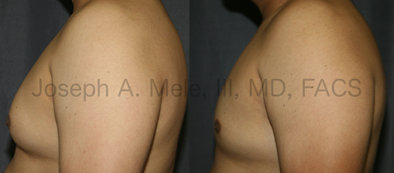
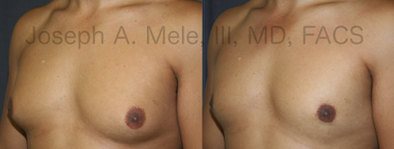
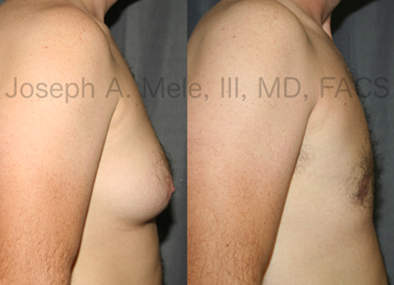
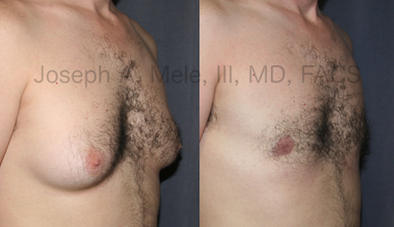
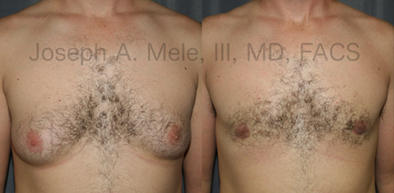
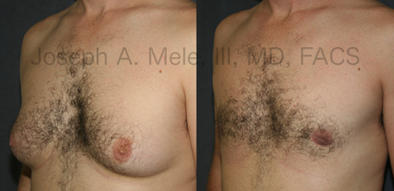
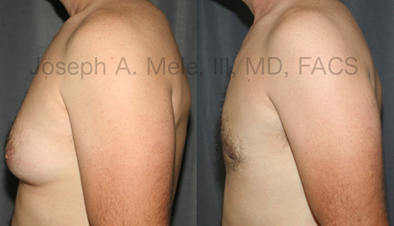
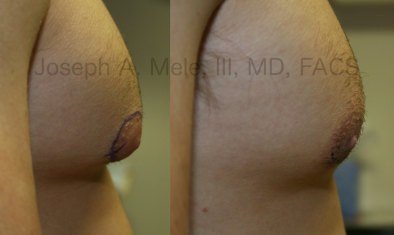
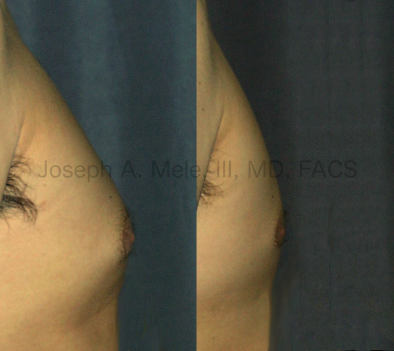
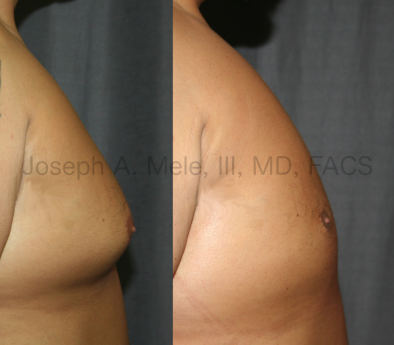
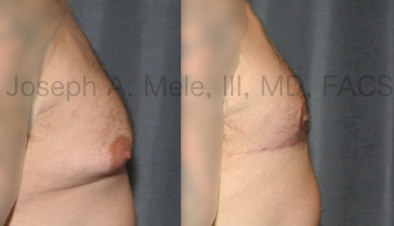
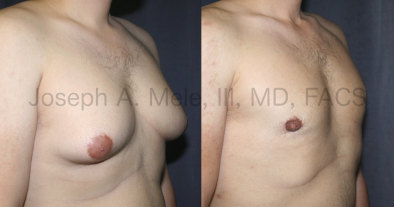
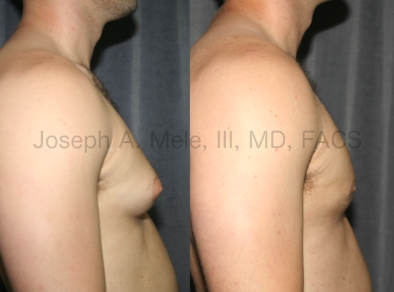
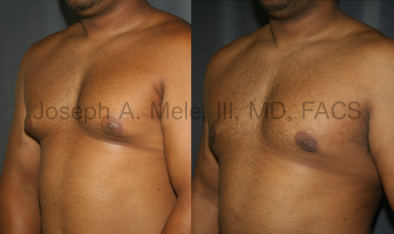
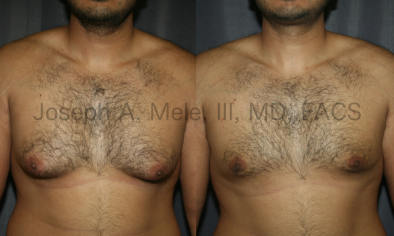
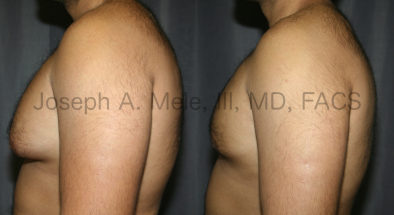
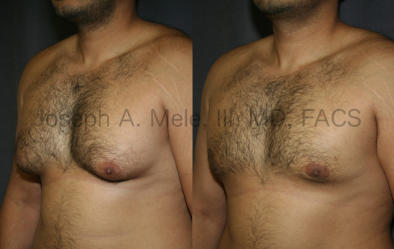
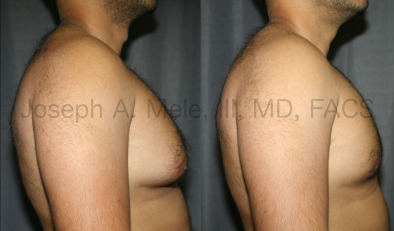
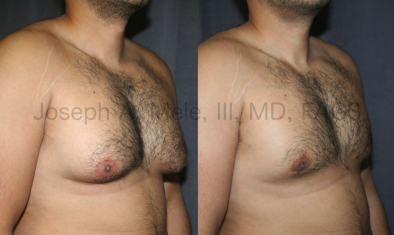
Types of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can be classified by type. Usual gynecomastia has two components: glandular tissue and fatty tissue. The glandular tissue is firm, rubber-like, and frequently tender. It is most commonly confined to the area behind the areola and nipple, but can encompass the entire breast in severe cases. The fatty tissue can also occur anywhere in the breast, but is most commonly concentrated in the lower breast. Fatty tissue is soft, so just like fat elsewhere in the body, it can often be removed with liposuction alone. The firm glandular tissue usually requires direct surgical removal.
Gynecomastia can be classified by location, size, cell type or age. Although not a medical term, moobs, the contraction of man boobs, has become a common term for gynecomastia. If you remember what gynecomastia means, moobs is technically more accurate. Here are some common medical terms for gynecomastia, and there are many more:
Gynecomastia classified by location or size
- Unilateral Gynecomastia – Gynecomastia only affecting one breast.
- Bilateral Gynecomastia – Gynecomastia of both breasts.
- Asymmetric Gynecomastia – Gynecomastia that affects both breasts, but is larger on one side. This is the most common morphology.
- Puffy Nipples – A common form of gynecomastia confined to the area beneath the areola, causing the nipple and areola to protrude. The more accurate term would be puffy areolae.
- Severe Gynecomastia – As the volume of the breasts increases, so does the skin. In cases of severe gynecomastia, the skin becomes lax and looses the ability to retract. Severe gynecomastia is more common in older men, and after massive weight gain and loss. Treatment usually includes removal of the excess breast tissue and may require additional incisions, resulting in scars, for the removal of the redundant skin.
Gynecomastia classified by cell type
- Gynecomastia is normally a combination of both glandular tissue and adipose (fat). The glandular breast tissue tends to be firm to hard and tender to touch. Adipose is soft and not usually tender. Sometimes one cell type predominates leading to purely glandular gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia. Both types are smoothed during Gynecomastia Reduction Surgery
- Purely Glandular – Purely glandular gynecomastia is seen in men with a low percent body fat. It is most often seen in body builders and other athletes. This type of gynecomastia is made up almost exclusively of firm glandular tissue. It can be the result of anabolic steroids, which are metabolized into estrogens. Since the tissue is firm and rubber-like, liposuction is not effective and is not usually necessary. A small periareolar incision is usually all that is required to treat this type of gynecomastia. Weight loss is not an effective treatment for purely glandular gynecomastia.
- Pseudogynecomastia – At the other end of the spectrum is pseudogynecomastia. Psuedogynecomastia is almost exclusively adipose. It gives the same appearance as gynecomastia; however, pseudogynecomastia is more amenable to diet and exercise and weight loss. The indications for the treatment of pseudogynecomastia are the same as the indication for liposuction elsewhere in the body. When diet and exercise are not effective, and the breast fullness remains disproportionate to the surrounding areas, liposuction can selectively remove the fat from the chest. Sometimes a nodule of glandular tissue maybe hidden in the fat tissue beneath the areolar. If present, the glandular tissue may require a small periareolar incision for removal.
Gynecomastia classified by cell type
- Gynecomastia is normally a combination of both glandular tissue and adipose (fat). The glandular breast tissue tends to be firm to hard and tender to touch. Adipose is soft and not usually tender. Sometimes one cell type predominates leading to purely glandular gynecomastia or pseudogynecomastia. Both types are smoothed during Gynecomastia Reduction Surgery
- Purely Glandular – Purely glandular gynecomastia is seen in men with a low percent body fat. It is most often seen in body builders and other athletes. This type of gynecomastia is made up almost exclusively of firm glandular tissue. It can be the result of anabolic steroids, which are metabolized into estrogens. Since the tissue is firm and rubber-like, liposuction is not effective and is not usually necessary. A small periareolar incision is usually all that is required to treat this type of gynecomastia. Weight loss is not an effective treatment for purely glandular gynecomastia.
- Pseudogynecomastia – At the other end of the spectrum is pseudogynecomastia. Psuedogynecomastia is almost exclusively adipose. It gives the same appearance as gynecomastia; however, pseudogynecomastia is more amenable to diet and exercise and weight loss. The indications for the treatment of pseudogynecomastia are the same as the indication for liposuction elsewhere in the body. When diet and exercise are not effective, and the breast fullness remains disproportionate to the surrounding areas, liposuction can selectively remove the fat from the chest. Sometimes a nodule of glandular tissue maybe hidden in the fat tissue beneath the areolar. If present, the glandular tissue may require a small periareolar incision for removal.
Gynecomastia classified by age
- Neonatal – Present at birth. Usually resolves without treatment.
- Adolescent – Occurs at puberty and affects more than half of all men ages 9 to 18. For half of these teens, adolescent gynecomastia will resolve in a few years. One third may have some degree of gynecomastia for the rest of their lives. Severe enlargement during adolescence may require surgical intervention.
- Adult – The most common form of gynecomastia occurs in adulthood.
Male Breast Reduction (Gynecomastia) Videos
Types of Gynecomastia Reduction Surgery
(Male Breast Reduction Surgery)
Below are listed the most common methods of Gynecomastia Reduction. Male Breast Reduction is different than Female Breast Reduction Surgery. The methods of gynecomastia reduction listed range from minor liposuction to complicated skin and gland reductions that may involve removing the nipple and areolae and replacing them higher on the chest. Dr. Mele will recommend specific procedures after a careful medical history and a focused physical examination are completed. If you want more information, call our Gynecomastia Specialist, Dr. Joseph Mele, in his Walnut Creek Plastic Surgery office, at (925) 943-6353, and schedule your private, confidential consultation. Alternatively, you can also use our convenient contact form.
Suction Assisted Lipectomy (SAL)
Liposuction is effective for removing fat. A minimal incision is sufficient for fat removal. As long as the skin tone is good, liposuction is the preferred Gynecomastia Reduction Surgery option for treating pseudogynecomastia. Tumescent Liposuction is the most commonly used method of treatment, and it can be preformed on an outpatient basis. Liposuction is not effective for the removal of the tough glandular tissue which frequently develops beneath the areola. To remove purely glandular gynecomastia, glandular resection is most effective.
Glandular Resection
The firm, glandular tissue that develops beneath the areola requires direct excision for removal. The best method of Male Breast Reduction Surgery for dense, subareolar gynecomastia is via a small, curved incision. An opening is made from four to eight o-clock, which is hidden along the lower edge of the pigmented areola. The Gynecomastia tissue is removed, and a layer of subcutaneous tissue is preserved beneath the areola to prevent indentation of the nipple. By tapering the edges of the gland while it’s removed, a smooth contour is created. When the gynecomastia also consists of adipose tissue, the fat often extends significantly past the edges of the pigmented skin of the areola. In these cases, Liposuction is used to remove the excess and further feather the edges.
Suction Assisted Lipectomy (SAL) with Glandular Resection
Often gynecomastia has both glandular and fatty components. The two methods above can be combined to give you optimal results. As long as the skin tone is good, liposuction combined with direct glandular resection, can safely and effectively reduce the chest, and create a more masculine contour.
Breast Skin Reduction
When the chest skin looses elasticity, it cannot shrink flat after gynecomastia is reduced. This can result in sagging. Redundant skin can fold over at the base of the breast and hang past the InfraMammary Fold (IMF). This is treated by surgically removing the excess skin. An incision is made in the IMF and the redundant skin is removed. If the skin is not overly redundant, the nipple and areola remain above the IMF. If the nipple and areola are below the IMF, a free nipple graft is indicated.
Free Nipple Grafts
For gynecomastia treatment, the nipple and areola are not usually removed; however, in certain situations a free nipple graft may provide the best results. If the chest skin is so redundant that the nipple hangs below the IMF, breast skin reduction as described above is indicated. However, removing the redundant skin means complete removal of the nipple and areola. The nipple and areola are replaced on the chest as a graft. A free nipple graft is much like a skin graft. Since no breast tissue needs to be preserved to keep the graft alive, a flatter, more masculine chest can be created. The down side is loss of nipple sensation. Some sensation can return with time, but the nipple is expected to remain less sensitive after grafting.
Male Breast Reduction Video Presentation
Gynecomastia Reduction Recovery
Gynecomastia Reduction Recovery will depend on the type of procedure required for the Gynecomastia Reduction. Simple excision and Liposuction will heal quickly, and most patients return to their normal activities in a few days to weeks. Major breast reductions, involving removal of excess breast gland, disproportionate chest fat and redundant saggy skin, require longer recoveries. When free nipple grafts are necessary, a longer period of immobilization is needed. Larger male breast reductions may require six weeks of recovery before full activity is allowed.
Gynecomastia Reduction Consultations
The best way to explore your Gynecomastia Reduction options is with an private, in-office consultation. During your appointment, Dr. Mele will review what needs to be done to get the best results. Your options, costs and recovery will be discussed in detail, so that you can feel confident in your decisions. To schedule a consultation appointment in our San Francisco Bay Area Plastic Surgery office call (925) 943-6353, or use our contact form.